Display Correct Aspect Ratio of Camera Preview in Android
In this post, we’ll dive into the key concepts and techniques for adjusting the size of a SurfaceView to match the camera preview’s aspect ratio and ensure a distortion-free display.
1. Orientation(s)
Before we get into the details, it’s important to first understand how orientation works in Android and how it affects camera previews.
1.1 Display Orientation
Display orientation describes the current rotation of the device screen. To obtain the orientation, we could use WindowManager.
1 | WindowManager windowManager = (WindowManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE); |
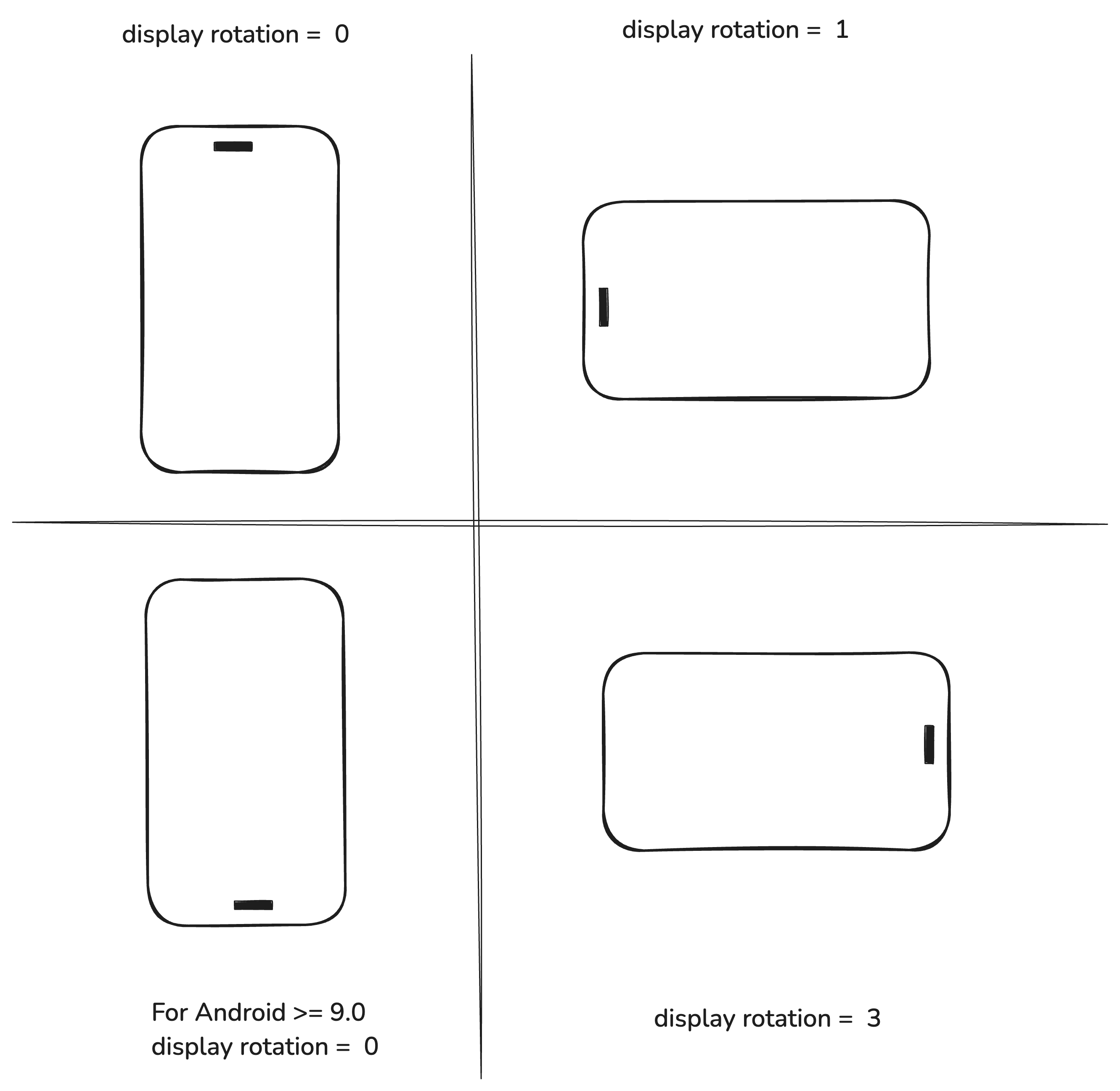
1.2 Camera Sensor Orientation
Camera sensor orientation refers to the angle between the physical orientation of the camera sensor and the device’s natural (unrotated) display orientation. This value is a fixed property of the camera hardware, and you can retrieve it like this:
1 | CameraManager manager = (CameraManager) context.getSystemService(Context.CAMERA_SERVICE); |
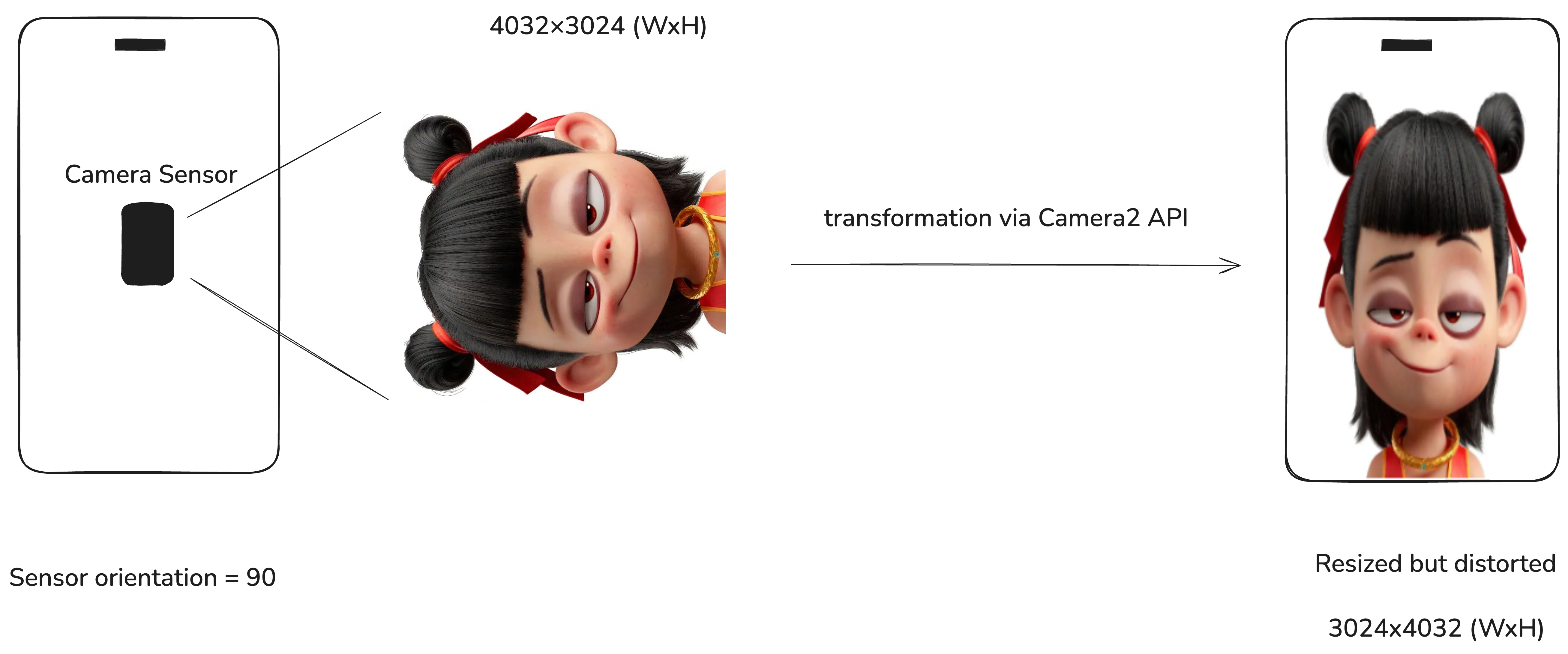
On most smartphones, the sensor orientation is 90 degrees. The image below illustrates what this actually means. Since the sensor is rotated 90 degrees relative to the screen, any image it captures will also be rotated accordingly.
When previewing with something like a SurfaceView, the Camera2 API compensates for this rotation automatically to ensure the image looks correct to the user. However, it does this by swapping the width and height of the preview buffer, which can lead to visual distortions—especially when the SurfaceView's aspect ratio doesn’t match the camera preview’s.
This automatic scaling often results in vertically stretched or squashed images, as shown below:
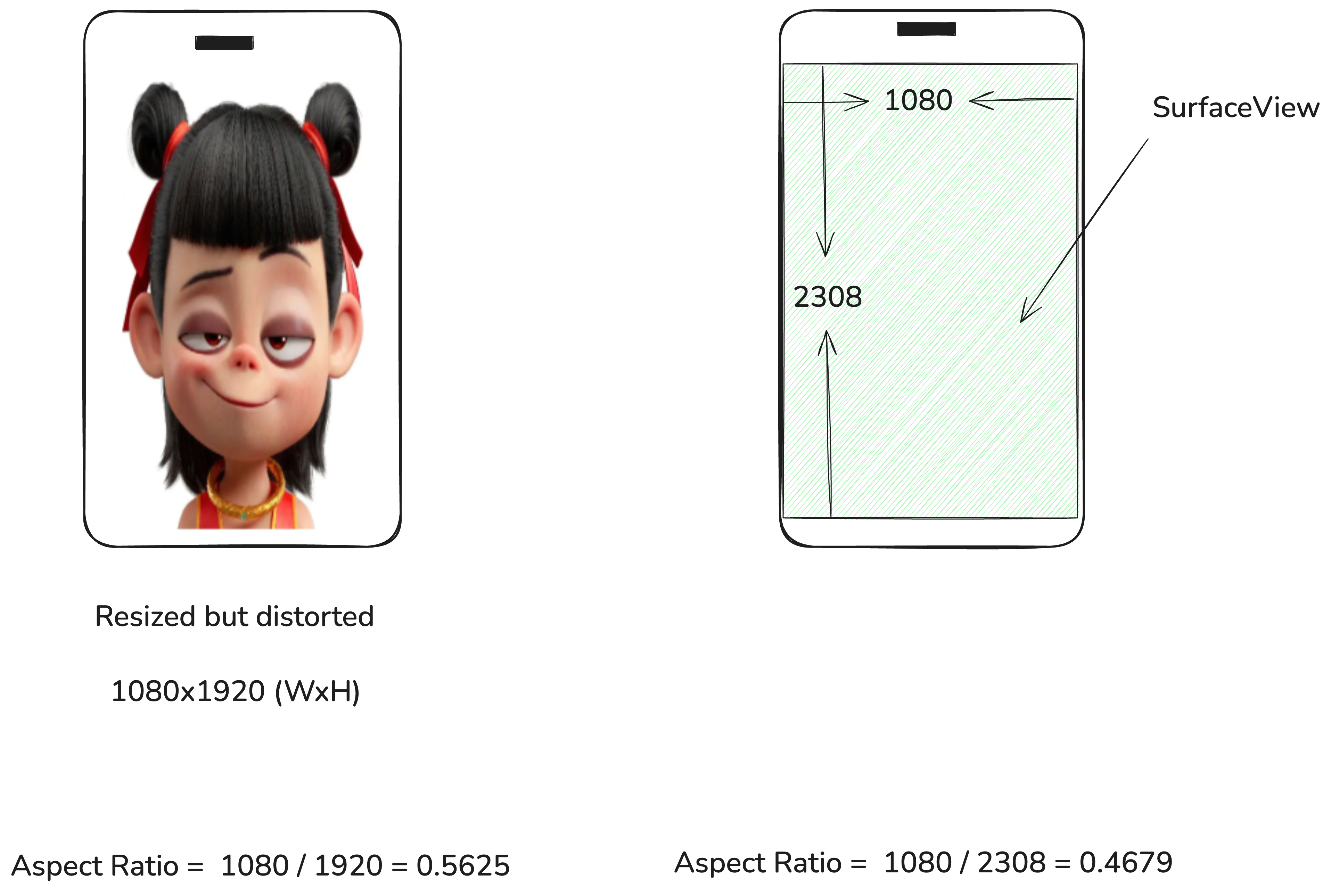
2. Root Cause of Distortion
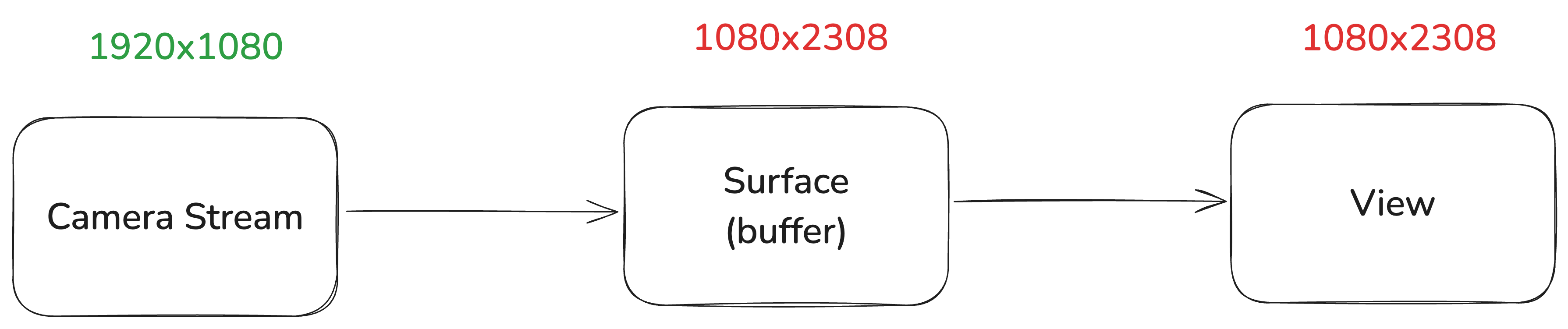
Let’s assume the image we capture from the image sensor is 1920x1080. The root cause of this problem is that the image size mismatches the SurfaceView size (1080x2308).
In Android, a SurfaceView is a special kind of View that provides a dedicated drawing surface embedded inside the view hierarchy. However, it’s a bit unique compared to regular views because it has a separate Surface that is managed independently by the window manager. By default, The Surface matches the size of the SurfaceView after layout is complete.
However, Surface can also have its own size. If the Surface buffer size is larger or smaller than the SurfaceView, scaling or clipping may occur.
Let’s rephrase the root cause in the context of SurfaceView and its associated Surface. By default, Surface has the same size as SurfaceView. And if we set SurfaceView to match the parent, then SurfaceView is determiend by its parent. For example:
1 | <FrameLayout |
Camera stream outputs images with size of 1920x1080 and renders to Surface‘s buffer. Since the buffer size is 1080x2308, the image will be resized at this stage. The buffer is then drawed on the View for display.
3. Solution
There are several ways to address this issue. In this post, I’ll present a simple and effective approach: center-crop. The core idea is to properly adjust the Surface buffer size and the View dimensions.
- Setting the correct
Surfacebuffer size ensures the received image isn’t resized or distorted. - Configuring the appropriate
Viewsize ensures the image is displayed with the correct aspect ratio.
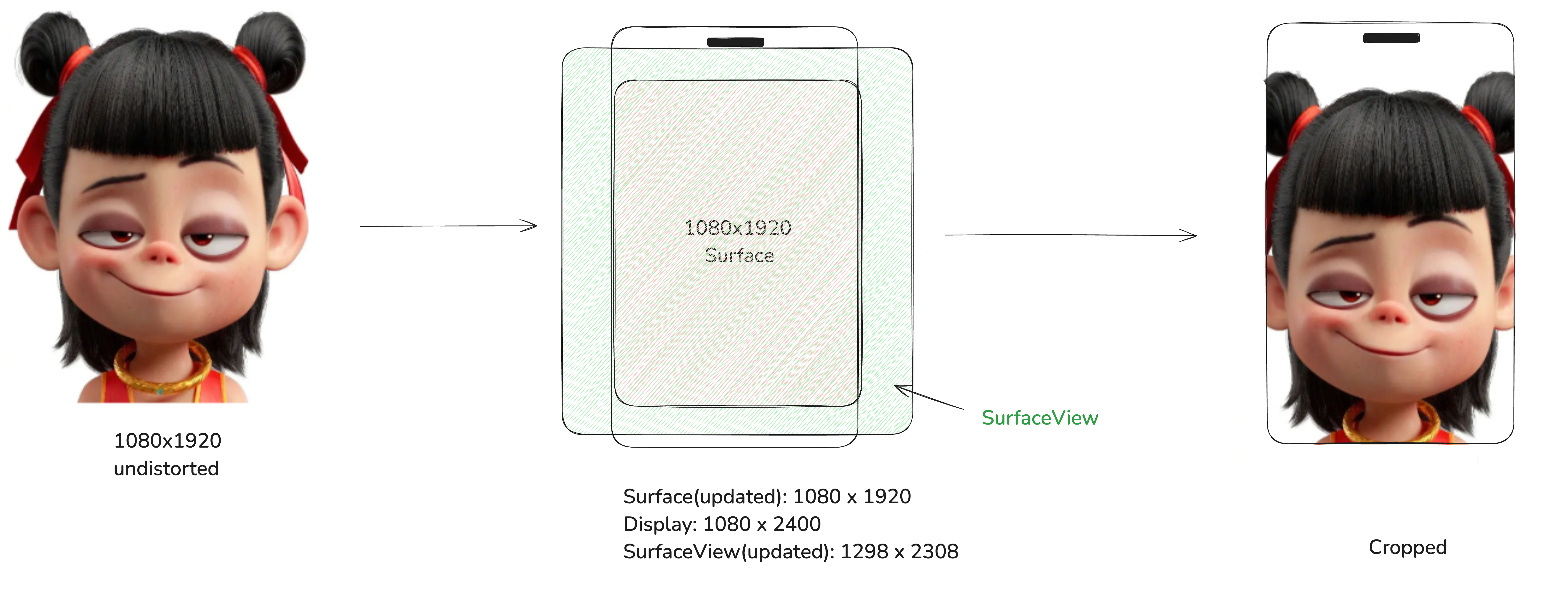
In order to display the original image with correct aspect ratio 1080/1920=0.5625, we fix Surface buffer size to be the same as image size. We also adjsut the View dimension to achieve the same aspect ratio. Here, we have two choices: either keep the short side or the long side. Keeping the short side will make the View smaller and leaving black space vertically. Keeping the long side will still fill up the entire screen but the preview is cropped at two sides.
We need a customized SurfaceView class.
1 | /** |
Display Correct Aspect Ratio of Camera Preview in Android
http://chuzcjoe.github.io/misc/misc-display-correct-aspect-ratio-camera-preview/
